Health
NIH Issues Advisory on Naegleria Amidst Rising Temperatures
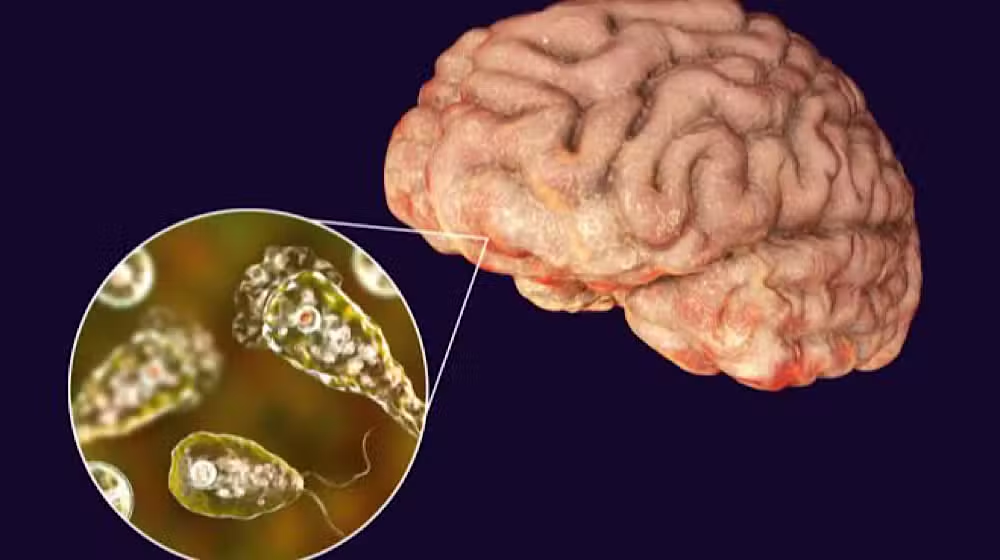
The National Institute of Health (NIH) has issued a crucial advisory regarding Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), commonly known as Naegleria or brain-eating amoeba, amidst rising temperatures and increased risk during the summer months.
Since 2008, cases of PAM-related deaths have been reported in several hospitals in Karachi during the summer season.
The advisory underscores the heightened risk of Naegleria fowleri infection during early summer due to elevated temperatures and inadequately chlorinated water.
ALSO EXPLORE
South Africa Beats Bangladesh in T20 World Cup Encounter
The primary objective of the advisory is to raise awareness among public health authorities, water and sanitation agencies, and relevant stakeholders to implement necessary measures for the prevention and control of PAM, particularly in regions with documented cases.
Naegleria fowleri, the amoeba responsible for PAM, thrives in warm, untreated water but cannot survive in clean, cool, and chlorinated water.
Chlorine is identified as the most effective method for disinfecting swimming pools and water systems, emphasizing the importance of proper water treatment and maintenance.
To mitigate the risk of infection, individuals are advised to avoid activities that involve jumping or diving into warm freshwater or thermal pools.
Furthermore, it is recommended to keep the head above water when using spas, thermal pools, or warm freshwater bodies.
ANOTHER STORY
Punjab Food Authority Seizes 800kg of Dead Chickens
Additionally, precautions should be taken with collapsible wading pools, which should be emptied and cleaned daily to prevent the accumulation of stagnant water conducive to amoeba growth.
Ensuring the adequate chlorination and maintenance of swimming pools and spas is imperative to reduce the risk of Naegleria fowleri contamination.
Individuals using untreated water sources are urged to refrain from allowing water to enter their noses during activities such as bathing, showering, or washing faces.
The advisory serves as a reminder of the importance of water safety practices, especially during the summer season when the risk of PAM transmission is heightened.
By adhering to these preventive measures, individuals can minimize the risk of infection and safeguard their health and well-being.








